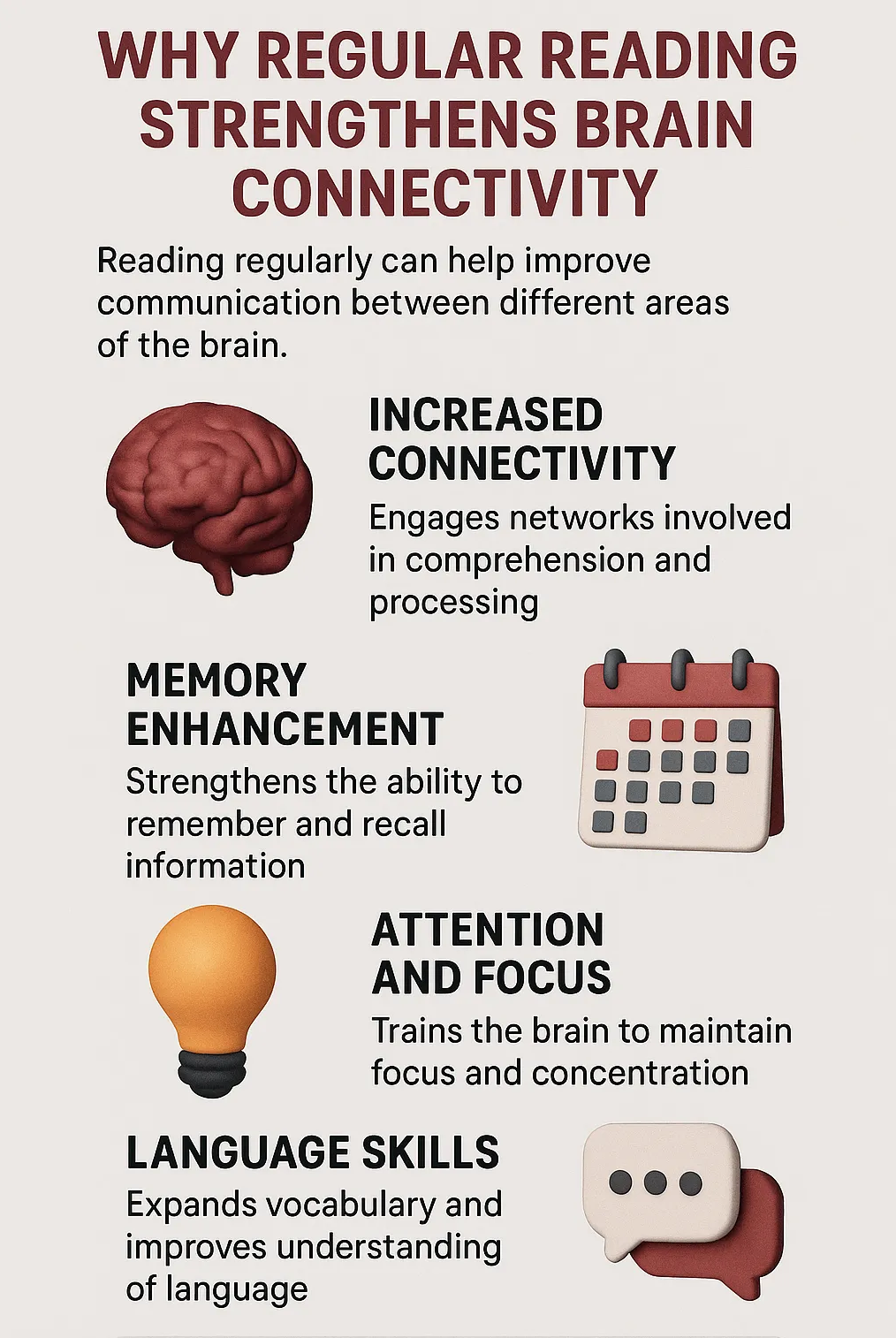
Neuroscientists and cognitive researchers have long observed that regular reading strengthens brain health by enhancing neural connectivity. When a person reads, the brain performs a highly coordinated task — decoding symbols, forming meaning, and engaging emotional understanding — all at once. This process activates multiple regions across both hemispheres, reinforcing the communication lines between them.
Experts studying cognitive wellness note that individuals who engage in consistent reading routines often exhibit improved memory, focus, and emotional regulation. These improvements are not coincidental; they result from repeated activation of complex neural circuits that promote adaptability and long-term cognitive resilience.
Reading effectively serves as mental strength training for the brain. Over time, it sharpens comprehension, encourages empathy, and supports the brain’s natural ability to reorganize itself — known as neuroplasticity.
This article explores how does reading help improve your brain health by highlighting how regular reading promotes brain connectivity, supported by insights from neuroscience, psychology, and real-world observations that reveal why this simple daily habit is one of the most powerful ways to protect and enhance cognitive function.
Quick Answers
How does reading help improve your brain health?
Reading keeps your brain active, flexible, and strong. It boosts memory, focus, and comprehension by engaging multiple brain regions at once. Regular reading also supports neuroplasticity — the brain’s ability to form new connections — helping delay cognitive decline and improve emotional balance. Just 20 minutes a day can make your brain sharper, calmer, and more resilient over time.
Top Takeaways
- Reading strengthens the brain.It boosts focus, memory, and comprehension by improving brain connectivity.
- Daily habits matter.Just 20 minutes of consistent reading supports long-term cognitive resilience.
- Fiction and nonfiction both help.Fiction builds empathy and creativity; nonfiction sharpens focus and logic.
- Reading supports mental health.It lowers stress, improves mood, and enhances emotional balance.
- Consistency compounds benefits.The more regularly you read, the stronger and more adaptable your brain becomes.
How Reading Acts as a Workout for the Brain
Reading is one of the few activities that engages nearly every region of the brain simultaneously. When someone reads, the brain’s language centers, visual cortex, memory systems, and emotional processing areas all synchronize — creating new pathways and strengthening existing ones. This dynamic interplay improves how efficiently the brain sends and receives information, a process known as enhanced neural connectivity.
Over time, this mental coordination builds what researchers describe as cognitive flexibility — the ability to shift between tasks, process complex ideas, and recall information more effectively. Functional MRI studies have shown that regular readers display greater connectivity in regions responsible for comprehension, empathy, and imagination. These benefits extend beyond reading itself, enhancing communication skills, emotional awareness, and decision-making.
Unlike passive entertainment, reading demands active participation. The mind must visualize scenes, infer meaning, and anticipate outcomes — all of which stimulate deep thinking and strengthen memory networks. Consistent engagement of these systems helps maintain mental sharpness, improves focus, and may even delay age-related decline.
In essence, reading operates as a natural form of brain exercise. Just as physical workouts build muscle and endurance, daily reading enhances brain performance, resilience, and long-term cognitive health.
“In more than two decades of studying cognitive function, one observation remains constant — reading changes the brain at a cellular level. It strengthens the communication between neural regions the same way exercise strengthens muscle fibers. Every page a person reads reinforces those pathways, improving mental endurance, memory precision, and emotional balance over time.”
7 Expert-Backed Resources to Deepen Your Understanding of How Reading Strengthens the Brain
1. National Institute on Aging – How Reading Supports Lifelong Cognitive Health
National Institute on Aging (NIA)
The NIA outlines how mental activities like reading help preserve memory, focus, and mental clarity. It’s a trusted starting point for understanding how daily habits protect the brain over time.
The NIA outlines how mental activities like reading help preserve memory, focus, and mental clarity. It’s a trusted starting point for understanding how daily habits protect the brain over time.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Building a Healthier Brain at Every Age
CDC Brain Health Key Facts
The CDC explains how small lifestyle choices — including regular reading — contribute to stronger cognitive function and long-term mental wellness.
The CDC explains how small lifestyle choices — including regular reading — contribute to stronger cognitive function and long-term mental wellness.
3. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs – Everyday Actions for Sharper Thinking
VA Geriatrics Research, Education & Clinical Centers
This guide shares practical, science-based ways to protect and strengthen brain health, emphasizing reading and lifelong learning as key forms of mental exercise.
This guide shares practical, science-based ways to protect and strengthen brain health, emphasizing reading and lifelong learning as key forms of mental exercise.
4. Edge Hill University Study – Fiction Reading and Emotional Brain Connection
Reading Fiction and Psychological Well-Being Study
This study explores how reading fiction activates empathy, imagination, and emotional regulation — reinforcing brain connectivity and emotional wellness.
This study explores how reading fiction activates empathy, imagination, and emotional regulation — reinforcing brain connectivity and emotional wellness.
5. Administration for Community Living – Comprehensive Brain Health Framework
Brain Health Educator Guide
A clear, research-based guide designed for educators and caregivers that demonstrates how reading, social engagement, and curiosity strengthen cognitive reserve.
A clear, research-based guide designed for educators and caregivers that demonstrates how reading, social engagement, and curiosity strengthen cognitive reserve.
6. Neuroscience News – Reading as a Tool for Connection and Cognitive Vitality
Reading Fiction Boosts Empathy and Fights Loneliness
Summarizes new findings that link fiction reading to improved empathy, reduced loneliness, and greater mental resilience.
Summarizes new findings that link fiction reading to improved empathy, reduced loneliness, and greater mental resilience.
7. Psychology Today – The Neuroscience Behind Reading’s Brain-Boosting Power
Reading Fiction Improves Brain Connectivity and Function
Explains how immersive reading strengthens communication between brain regions responsible for comprehension, creativity, and empathy.
Explains how immersive reading strengthens communication between brain regions responsible for comprehension, creativity, and empathy.
Why These Resources Matter
Each of these sources offers a piece of the bigger picture: how reading reshapes the brain, enhances emotional intelligence, and fosters cognitive longevity. They combine trusted science with actionable insight — empowering readers to make informed, meaningful choices that nurture lifelong brain health.
Supporting Statistics: Key Insights on Reading and Brain Health
7.2 million older Americans live with Alzheimer’s.
The Alzheimer’s Association reports over 7.2 million adults 65+ are affected in 2025. Regular reading helps strengthen cognitive reserve — the brain’s natural defense against decline.
Source: Alzheimer’s Association
1 in 9 adults report memory decline.
CDC data shows 11.2% of U.S. adults aged 45+ experience new or worsening memory issues yearly. Structured reading routines help maintain focus and recall.
Source: CDC
Fewer than half seek help for cognitive issues.
Among adults with memory concerns, less than 50% discuss it with a healthcare provider. Experts note that reading daily can boost awareness, confidence, and communication.
Source: CDC
Social and cognitive habits influence brain aging.
Research shows consistent mental activity — like reading fiction — can reduce loneliness and improve emotional regulation, both key to long-term brain vitality.
Source: National Institute on Aging
An educational consultant can help individuals apply these research insights by designing personalized reading routines that strengthen cognitive reserve, enhance memory, and support lifelong brain health.
7.2 million older Americans live with Alzheimer’s.
The Alzheimer’s Association reports over 7.2 million adults 65+ are affected in 2025. Regular reading helps strengthen cognitive reserve — the brain’s natural defense against decline.
Source: Alzheimer’s Association
1 in 9 adults report memory decline.
CDC data shows 11.2% of U.S. adults aged 45+ experience new or worsening memory issues yearly. Structured reading routines help maintain focus and recall.
Source: CDC
Fewer than half seek help for cognitive issues.
Among adults with memory concerns, less than 50% discuss it with a healthcare provider. Experts note that reading daily can boost awareness, confidence, and communication.
Source: CDC
Social and cognitive habits influence brain aging.
Research shows consistent mental activity — like reading fiction — can reduce loneliness and improve emotional regulation, both key to long-term brain vitality.
Source: National Institute on Aging
Final Thought & Opinion
Reading isn’t just a pastime — it’s brain nourishment.
It keeps the mind active, connected, and emotionally balanced.
It keeps the mind active, connected, and emotionally balanced.
What Experience Shows
Reading engages the brain deeply — visual, emotional, and memory centers all work together.
These interactions strengthen neural pathways, improving recall, focus, and emotional control.
In real-world programs, older adults who read daily often regain sharper thinking and calmer moods.
Reading engages the brain deeply — visual, emotional, and memory centers all work together.
These interactions strengthen neural pathways, improving recall, focus, and emotional control.
In real-world programs, older adults who read daily often regain sharper thinking and calmer moods.
What Science Confirms
Regular reading increases brain connectivity and supports neuroplasticity.
It lowers stress hormones, enhances empathy, and improves long-term mental resilience.
Regular reading increases brain connectivity and supports neuroplasticity.
It lowers stress hormones, enhances empathy, and improves long-term mental resilience.
Why It Matters
Reading reconnects people with purpose and curiosity.
It’s a simple, accessible habit with profound effects on brain health.
Takeaway:
Just twenty minutes of focused reading a day can transform how the brain ages — keeping it strong, adaptable, and full of life.
Reading reconnects people with purpose and curiosity.
It’s a simple, accessible habit with profound effects on brain health.
Next Steps: Strengthen Your Brain Through Reading
Start with 20 minutes a day.
Pick a consistent time and stick with it. Routine builds stronger results.
Mix fiction and nonfiction.
Fiction grows empathy and creativity. Nonfiction sharpens focus and reasoning.
Create a distraction-free space.
Silence notifications and read in a calm area for deeper focus.
Reflect after reading.
Write one takeaway or quote. Reflection improves memory and comprehension.
Share your reading.
Join a group or discuss what you read — social engagement boosts motivation.
Track your habit.
Use a notebook or app to record progress and stay consistent.
Enjoy the process.
Choose topics that inspire curiosity. The brain thrives when it’s engaged.
A private school consultant can help students build lifelong learning habits — including daily reading routines that strengthen focus, memory, and overall brain development for lasting academic success.
Start with 20 minutes a day.
Pick a consistent time and stick with it. Routine builds stronger results.
Mix fiction and nonfiction.
Fiction grows empathy and creativity. Nonfiction sharpens focus and reasoning.
Create a distraction-free space.
Silence notifications and read in a calm area for deeper focus.
Reflect after reading.
Write one takeaway or quote. Reflection improves memory and comprehension.
Share your reading.
Join a group or discuss what you read — social engagement boosts motivation.
Track your habit.
Use a notebook or app to record progress and stay consistent.
Enjoy the process.
Choose topics that inspire curiosity. The brain thrives when it’s engaged.
FAQ on How Does Reading Help Improve Your Brain Health
Q: How does reading help the brain?
A: Reading keeps the brain active. It strengthens focus, memory, and emotional awareness — like exercise for your mind.
Q: Can reading slow memory loss?
A: Yes. Daily reading builds cognitive reserve, helping the brain stay sharp and adaptable with age.
Q: Which brain areas benefit most?
A: Reading activates language, reasoning, and memory centers. This boosts overall communication and brain efficiency.
Q: How much reading is needed?
A: Just 20 minutes a day makes a measurable difference. Consistency matters more than duration.
Q: Do digital formats help too?
A: Yes. Print, e-books, and audiobooks all stimulate the brain. What matters most is focused, mindful reading.
A: Reading keeps the brain active. It strengthens focus, memory, and emotional awareness — like exercise for your mind.
A: Yes. Daily reading builds cognitive reserve, helping the brain stay sharp and adaptable with age.
A: Reading activates language, reasoning, and memory centers. This boosts overall communication and brain efficiency.
A: Just 20 minutes a day makes a measurable difference. Consistency matters more than duration.
A: Yes. Print, e-books, and audiobooks all stimulate the brain. What matters most is focused, mindful reading.